Bootstrap Layout Tutorial
Introduction
In the recent several years the mobile gadgets developed into such critical element of our lives that the majority of us can't actually imagine how we got to get around without needing them and this is being stated not simply for phoning others by talking just as if you remember was really the original goal of the mobiles but in fact linking with the entire world by featuring it directly in your arms. That is definitely the key reason why it likewise ended up being very important for the most usual habitants of the Web-- the web pages have to showcase as fantastic on the compact mobile displays as on the standard desktop computers that at the same time got even wider making the size difference also greater. It is presumed somewhere at the starting point of all this the responsive systems come down to pop up supplying a practical strategy and a handful of brilliant tools for getting pages behave despite the device viewing them.
But what's very likely most important and stocks the structures of so called responsive website design is the treatment in itself-- it's entirely different from the one we used to have actually for the corrected width webpages from the very last several years which consequently is a lot just like the one in the world of print. In print we do have a canvas-- we set it up once initially of the project to improve it up perhaps a number of times since the work proceeds yet at the basic line we finish up with a media of size A and art work with size B positioned on it at the indicated X, Y coordinates and that is really it-- once the project is handled and the sizes have been adjusted all of it ends.
In responsive website design but there is simply no such thing as canvas size-- the possible viewport dimensions are as basically infinite so establishing a fixed value for an offset or a size can be wonderful on one screen but quite irritating on another-- at the other and of the specter. What the responsive frameworks and especially some of the most well-known of them-- Bootstrap in its own current fourth edition provide is some creative ways the web pages are being actually created so they automatically resize and also reorder their particular components adjusting to the space the viewing display screen provides and not moving far from its width-- in this manner the site visitor reaches scroll only up/down and gets the web content in a helpful scale for studying free from having to pinch zoom in or out in order to see this part or another. Let's see exactly how this normally works out. ( learn more here)
Exactly how to put into action the Bootstrap Layout Grid:
Bootstrap incorporates numerous components and possibilities for laying out your project, incorporating wrapping containers, a strong flexbox grid system, a versatile media things, and responsive utility classes.
Bootstrap 4 framework works with the CRc structure to take care of the webpage's web content. Assuming that you are actually just starting this the abbreviation makes it simpler to keep in mind considering that you are going to possibly sometimes ask yourself at first which component provides what. This come for Container-- Row-- Columns that is the structure Bootstrap framework utilizes intended for making the web pages responsive. Each responsive web page features containers holding usually a single row with the needed quantity of columns inside it-- all of them together making a significant web content block on web page-- just like an article's heading or body , list of material's components and so on.
Let's look at a single web content block-- like some elements of what ever being actually provided out on a page. First we really need wrapping the whole detail in a
.container.container-fluidNext inside of our
.container.rowThese are used for handling the placement of the content components we set within. Considering that newest alpha 6 version of the Bootstrap 4 framework utilizes a styling approach named flexbox with the row element now all variety of placements setup, grouping and sizing of the web content can be attained with simply including a simple class but this is a complete new story-- for right now do understand this is actually the component it is actually performed with.
Lastly-- within the row we should install certain
.col-Basic styles
Containers are actually probably the most simple design element in Bootstrap and are demanded whenever employing default grid system. Select from a responsive, fixed-width container (meaning its own
max-width100%Even though containers can be nested, a large number of Bootstrap Layouts configurations do not require a embedded container.
<div class="container">
<!-- Content here -->
</div>Apply
.container-fluid
<div class="container-fluid">
...
</div>Check out some responsive breakpoints
Since Bootstrap is established to be mobile first, we work with a fistful of media queries to produce sensible breakpoints for interfaces and styles . These types of breakpoints are mostly based on minimum viewport sizes and make it possible for us to size up elements just as the viewport modifications .
Bootstrap mostly uses the following media query ranges-- as well as breakpoints-- in Sass files for format, grid structure, and components.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
// No media query since this is the default in Bootstrap
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...As we create source CSS with Sass, all of the Bootstrap media queries are actually obtainable via Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-up(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(xl) ...
// Example usage:
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm)
.some-class
display: block;We from time to time employ media queries that proceed in the various other way (the provided screen size or more compact):
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, less than 768px)
@media (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, less than 992px)
@media (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, less than 1200px)
@media (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops)
// No media query since the extra-large breakpoint has no upper bound on its widthOnce again, these types of media queries are in addition provided through Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-down(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(lg) ...There are likewise media queries and mixins for focus on a single section of screen sizes employing the minimum required and maximum breakpoint widths.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) and (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...These types of media queries are also provided by means of Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-only(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(xl) ...Likewise, media queries may perhaps extend numerous breakpoint sizes:
// Example
// Apply styles starting from medium devices and up to extra large devices
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...The Sass mixin for targeting the exact display screen size range would certainly be:
@include media-breakpoint-between(md, xl) ...Z-index
Some Bootstrap components apply
z-indexWe do not support modification of these types of values; you alter one, you most likely require to switch them all.
$zindex-dropdown-backdrop: 990 !default;
$zindex-navbar: 1000 !default;
$zindex-dropdown: 1000 !default;
$zindex-fixed: 1030 !default;
$zindex-sticky: 1030 !default;
$zindex-modal-backdrop: 1040 !default;
$zindex-modal: 1050 !default;
$zindex-popover: 1060 !default;
$zindex-tooltip: 1070 !default;Background components-- such as the backdrops which make it possible for click-dismissing-- have the tendency to reside on a low
z-indexz-indexOne more recommendation
Using the Bootstrap 4 framework you have the ability to create to five separate column appeals according to the predefined in the framework breakpoints however usually 2 to 3 are quite sufficient for attaining ideal appeal on all of the display screens. ( find more)
Final thoughts
So right now hopefully you do possess a general idea what responsive web site design and frameworks are and just how one of the most famous of them the Bootstrap 4 framework works with the webpage web content in order to make it display best in any screen-- that's just a fast peek but It's believed the understanding just how the things do a job is the greatest base one should step on just before digging in to the details.
Examine several on-line video short training regarding Bootstrap layout:
Connected topics:
Bootstrap layout official documents

A method inside Bootstrap 4 to specify a desired format
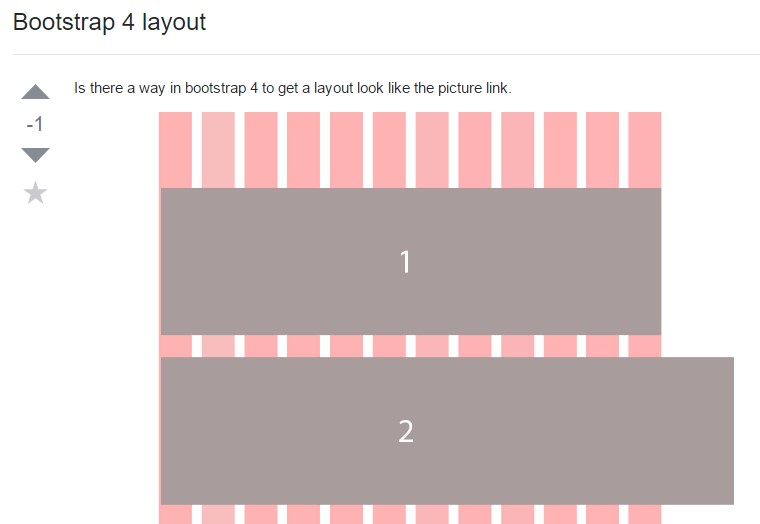
Layout illustrations inside of Bootstrap 4