Bootstrap Breakpoints Working
Overview
Accepting in consideration all of the feasible display screen sizes in which our online pages could ultimately feature it is important to design them in a way offering universal understandable and strong visual appeal-- normally applying the assistance of a effective responsive framework like one of the most well-known one-- the Bootstrap framework in which current version is right now 4 alpha 6. However, what it actually does to help the web pages appear great on any kind of display screen-- let's have a look and observe.
The fundamental idea in Bootstrap as a whole is positioning some order in the limitless possible gadget screen widths (or viewports) putting them in a handful of ranges and styling/rearranging the web content properly. These are additionally termed grid tiers or display sizes and have progressed quite a little throughout the different editions of the most famous lately responsive framework around-- Bootstrap 4. ( click this)
Ways to employ the Bootstrap Breakpoints Responsive:
Ordinarily the media queries get defined with the following structure
@media ( ~screen size condition ~) ~ styling rules to get applied if the condition is met ~min-width: 768pxmin-width: 768pxImprovements of Bootstrap editions
Within Bootstrap 4 compared to its own predecessor there are actually 5 display screen sizes but considering that the latest alpha 6 build-- simply just 4 media query groups-- we'll get back to this in just a sec. Considering that you most probably know a
.row.col -Screen measurements
The screen sizes in Bootstrap generally use the
min-widthExtra small – widths under 576px –This screen actually doesn't have a media query but the styling for it rather gets applied as a common rules getting overwritten by the queries for the widths above. What's also new in Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it actually doesn't use any size infix – so the column layout classes for this screen size get defined like
col-6Extra small-- widths less than 576px-- This screen actually does not provide a media query but the styling for it instead gets employed as a standard regulations becoming overwritten by the queries for the widths above. What is really likewise brand-new in Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it actually does not make use of any scale infix-- and so the column design classes for this specific display dimension get determined such as
col-6Small screens-- works with
@media (min-width: 576px) ...-sm-.col-sm-6Medium displays-- works with
@media (min-width: 768px) ...-md-.col-md-6Large displays - uses
@media (min-width: 992px) ...-lg-And and finally-- extra-large displays -
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...-xl-Responsive breakpoints
Considering Bootstrap is actually developed to become mobile first, we use a small number of media queries to establish sensible breakpoints for designs and programs . These types of Bootstrap Breakpoints Responsive are mainly founded on minimal viewport widths as well as make it possible for us to graduate up factors just as the viewport changes. ( read more here)
Bootstrap primarily makes use of the following media query ranges-- or breakpoints-- in source Sass files for design, grid structure, and elements.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
// No media query since this is the default in Bootstrap
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...Since we create resource CSS in Sass, all of media queries are readily available by means of Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-up(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(xl) ...
// Example usage:
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm)
.some-class
display: block;We sometimes use media queries which perform in the additional direction (the supplied display dimension or even scaled-down):
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, less than 768px)
@media (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, less than 992px)
@media (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, less than 1200px)
@media (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops)
// No media query since the extra-large breakpoint has no upper bound on its widthOnce more, these particular media queries are additionally obtainable via Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-down(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(lg) ...There are likewise media queries and mixins for targeting a single segment of display screen dimensions working with the minimum and highest Bootstrap Breakpoints Using widths.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) and (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...These types of media queries are additionally attainable via Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-only(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(xl) ...Similarly, media queries may span multiple breakpoint sizes:
// Example
// Apply styles starting from medium devices and up to extra large devices
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
<code/>
The Sass mixin for aim at the similar display screen scale variation would certainly be:
<code>
@include media-breakpoint-between(md, xl) ...Final thoughts
Along with specifying the size of the web page's elements the media queries occur all around the Bootstrap framework usually becoming determined by it
- ~screen size ~Review a number of on-line video information about Bootstrap breakpoints:
Linked topics:
Bootstrap breakpoints main information

Bootstrap Breakpoints problem
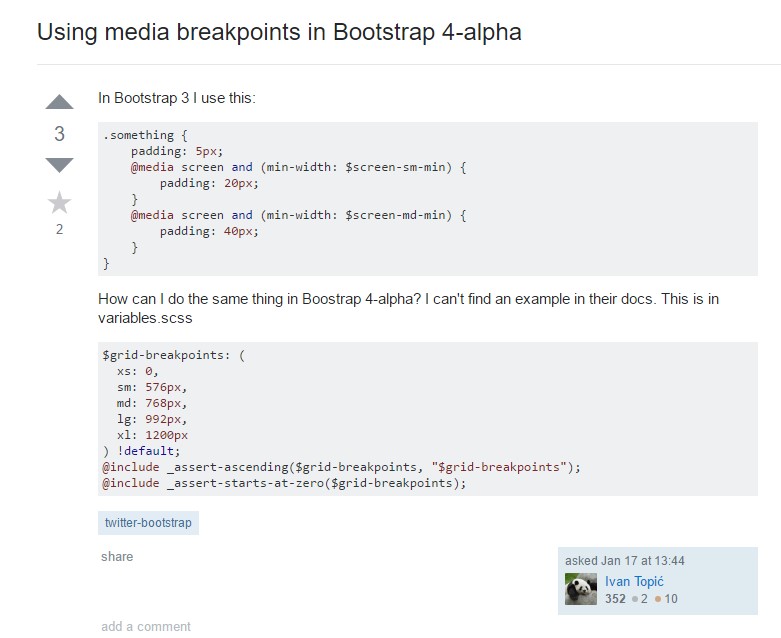
Modify media query breakpoint systems from 'em' to 'px'